OAS Clawback 2025: What Retirees Need to Know About the Recovery Tax
OAS Clawback 2025
If you’ve worked hard to build your retirement income, the last thing you want is to see your government benefits clawed back. Yet for many Canadians, the Old Age Security (OAS) recovery tax—commonly called the OAS clawback—can quietly reduce this valuable benefit.
Here’s how the recovery tax works in 2025, what happens if you delay OAS to age 70, and the strategies we use to help our clients minimize or avoid the clawback.
What is the OAS Recovery Tax?
OAS is a monthly benefit available to most Canadians aged 65 and older. However, once your income exceeds a certain level, the government recovers part or all of your OAS through the recovery tax.
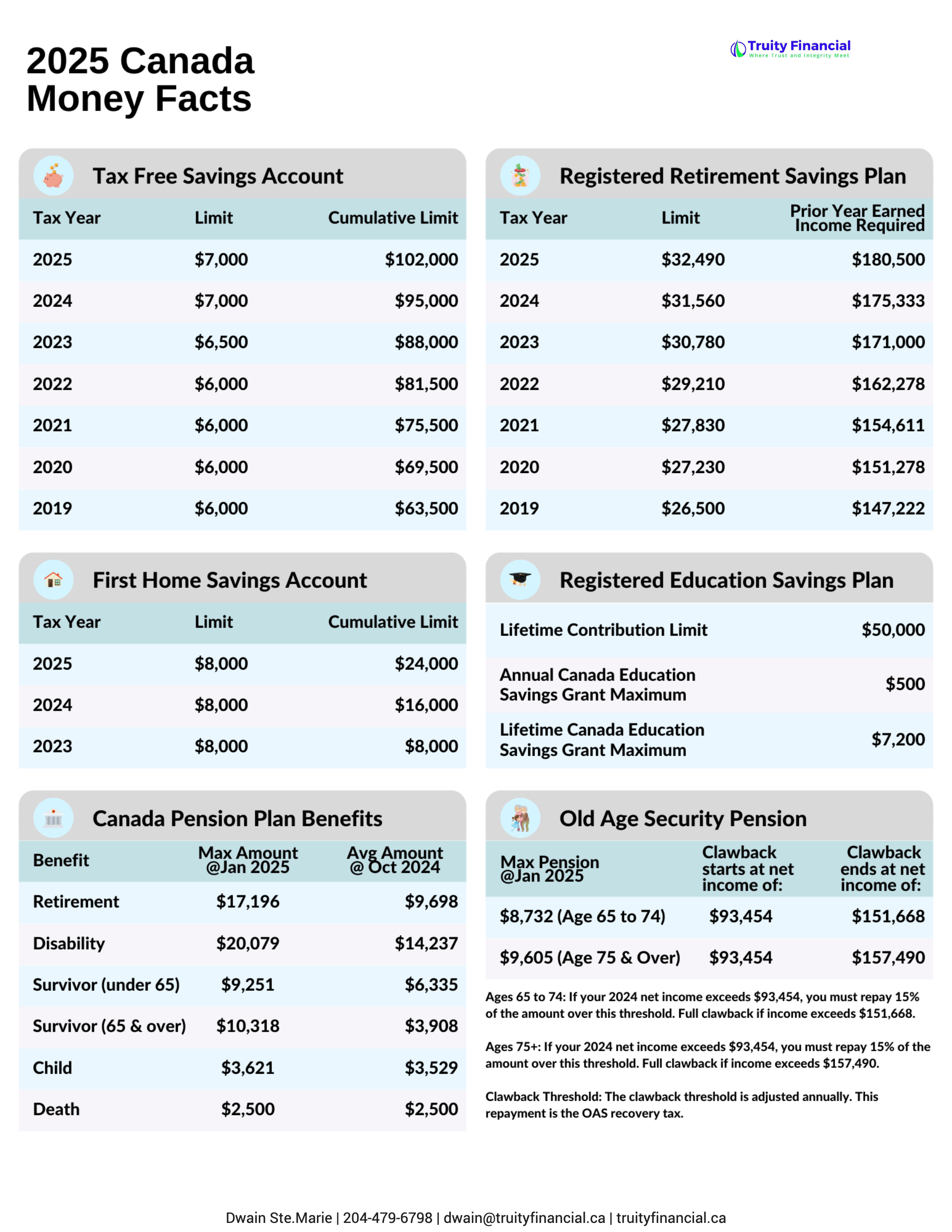
This is calculated based on Line 23400 of your tax return—net income before adjustments. In 2025, the clawback begins when your income exceeds $93,454. For every dollar above that amount, you must repay 15 cents of your OAS.
If your income reaches approximately $151,668 (age 65–74) or $157,490 (age 75+), you could lose your entire OAS benefit for the year.
How Much is the OAS Benefit in 2025?
From July through September 2025, the maximum monthly OAS payment is:
-
$734.95 for individuals aged 65–74 (about $8,820 annually)
-
$808.45 for individuals aged 75+ (reflecting a 10% enhancement introduced in 2022)
These amounts are indexed quarterly to inflation and are subject to clawback if your Line 23400 income exceeds the threshold.
What Happens if You Delay OAS Until 70?
You can choose to delay receiving OAS up to age 70, increasing your monthly benefit by 0.6% for each month deferred—a total boost of up to 36% if you wait the full five years.
While a higher payment may sound appealing, it can also lead to larger OAS repayments if your income—including CPP, investment returns, or pension income—exceeds the recovery threshold. Delaying OAS often makes sense for healthy individuals who expect to live into their late 80s or beyond and have lower taxable income during the deferral period.
How the OAS Recovery Tax Works
Example: Alan is 68 and receives the maximum OAS: $8,820 annually. In 2025, the clawback threshold begins at $93,454. Alan’s line 23400 income is $100,000—that’s $6,546 over the clawback threshold. As a result, he must repay: $6,546 × 15% = $981.90
This leaves Alan with $7,838.10 in OAS benefits for the year. If he earns more, the repayment increases proportionally. Once Alan’s income reaches around $151,668 (if aged 65–74) or $157,490 (if aged 75+), his entire OAS would be clawed back.
The recovery tax calculation is automatic and appears on your Notice of Assessment each spring, adjusting your OAS payments for the following July–June period.
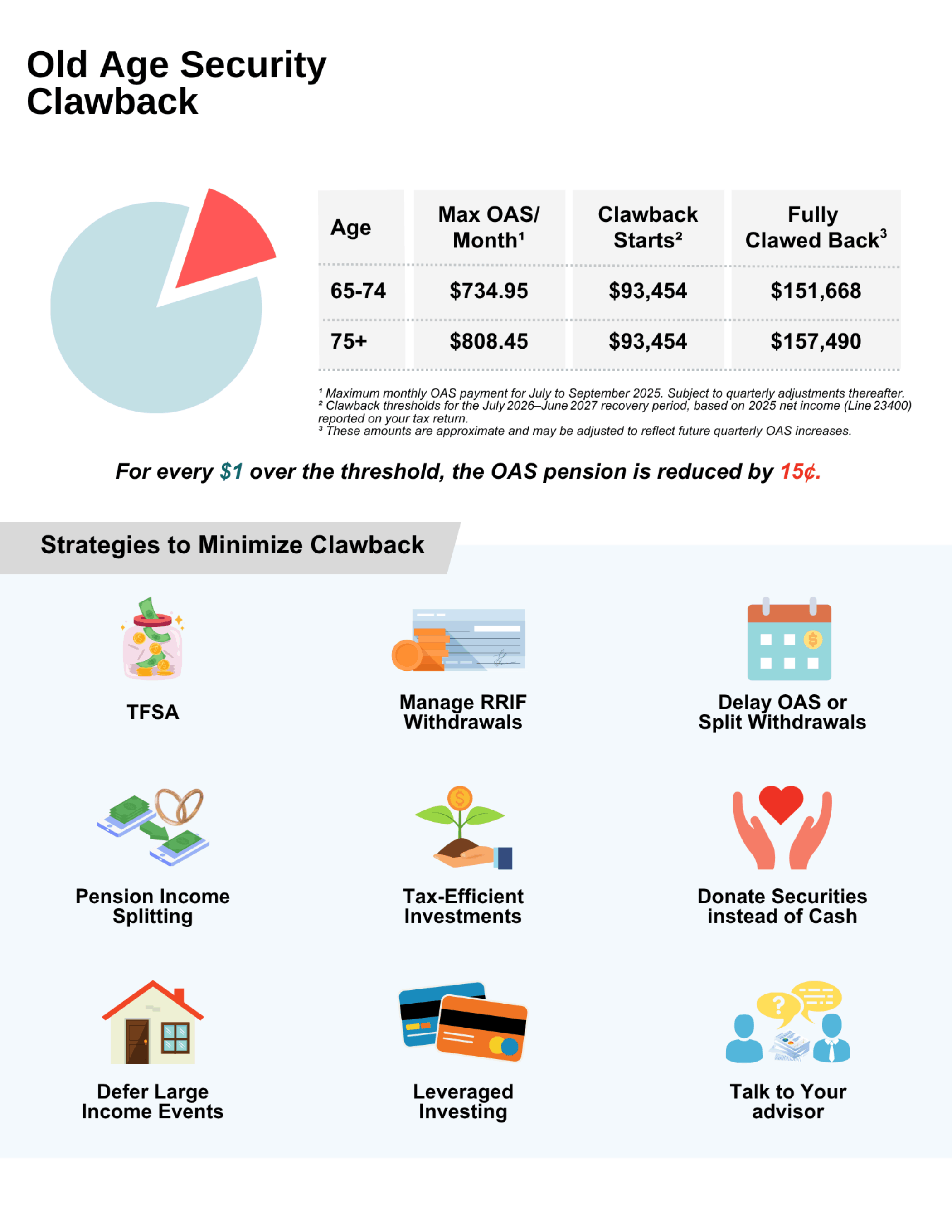
Strategies to Reduce or Avoid the OAS Clawback
The good news? There are practical ways to lower your Line 23400 income without compromising your lifestyle. Here are some of the strategies we use to help our clients keep more of their benefits:
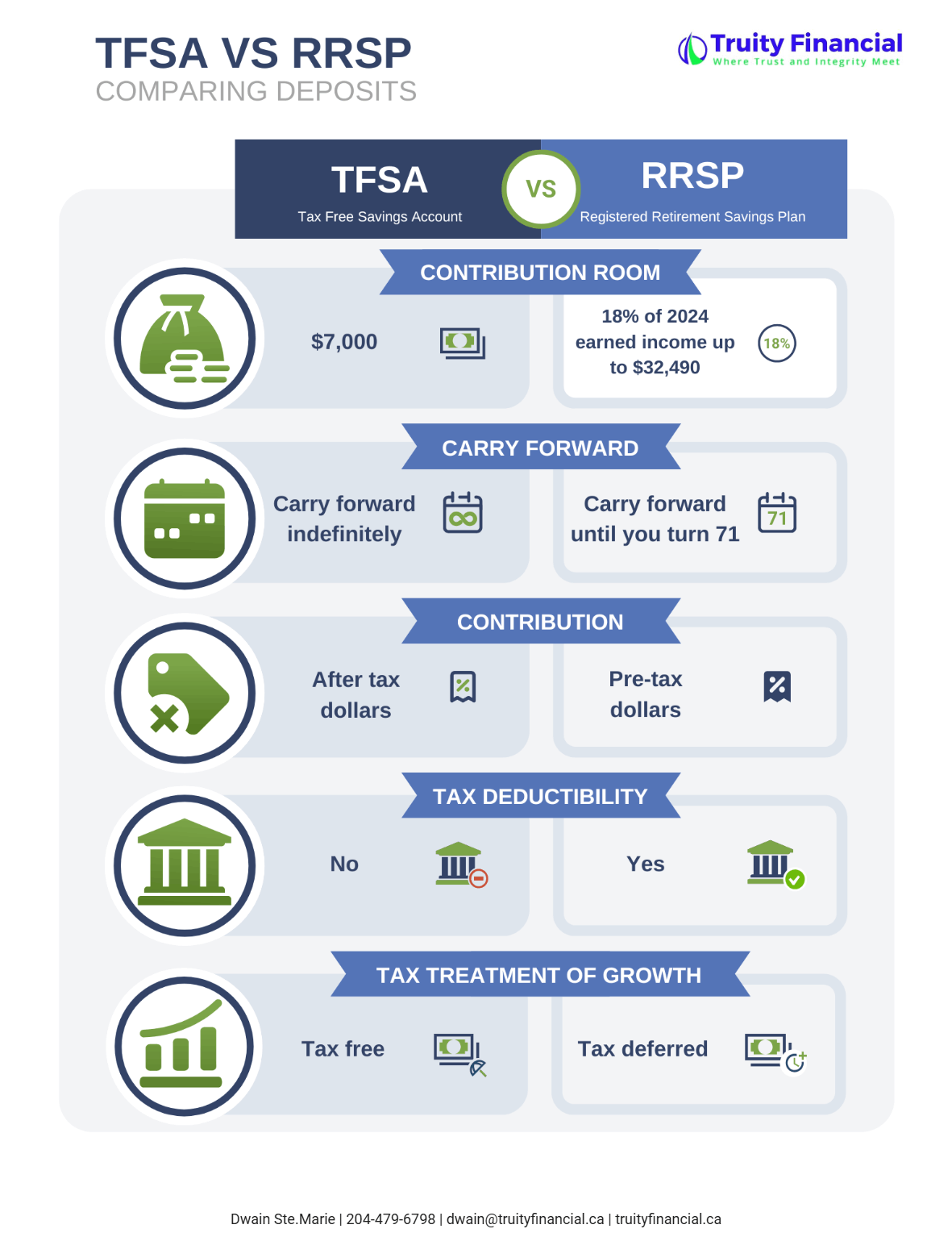
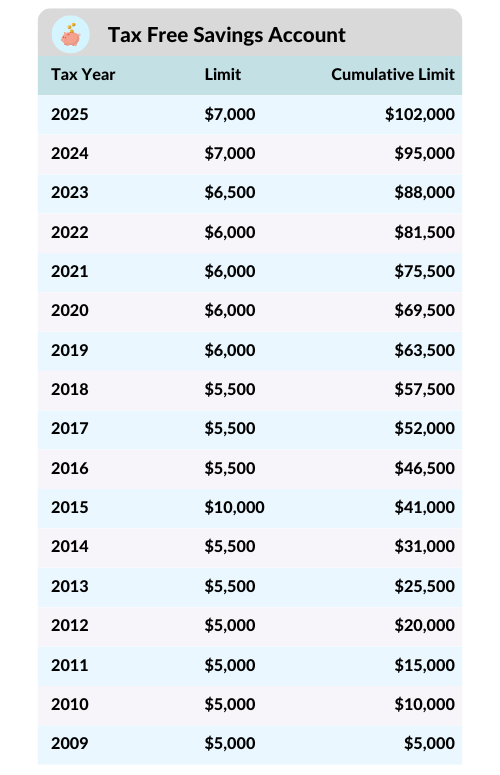
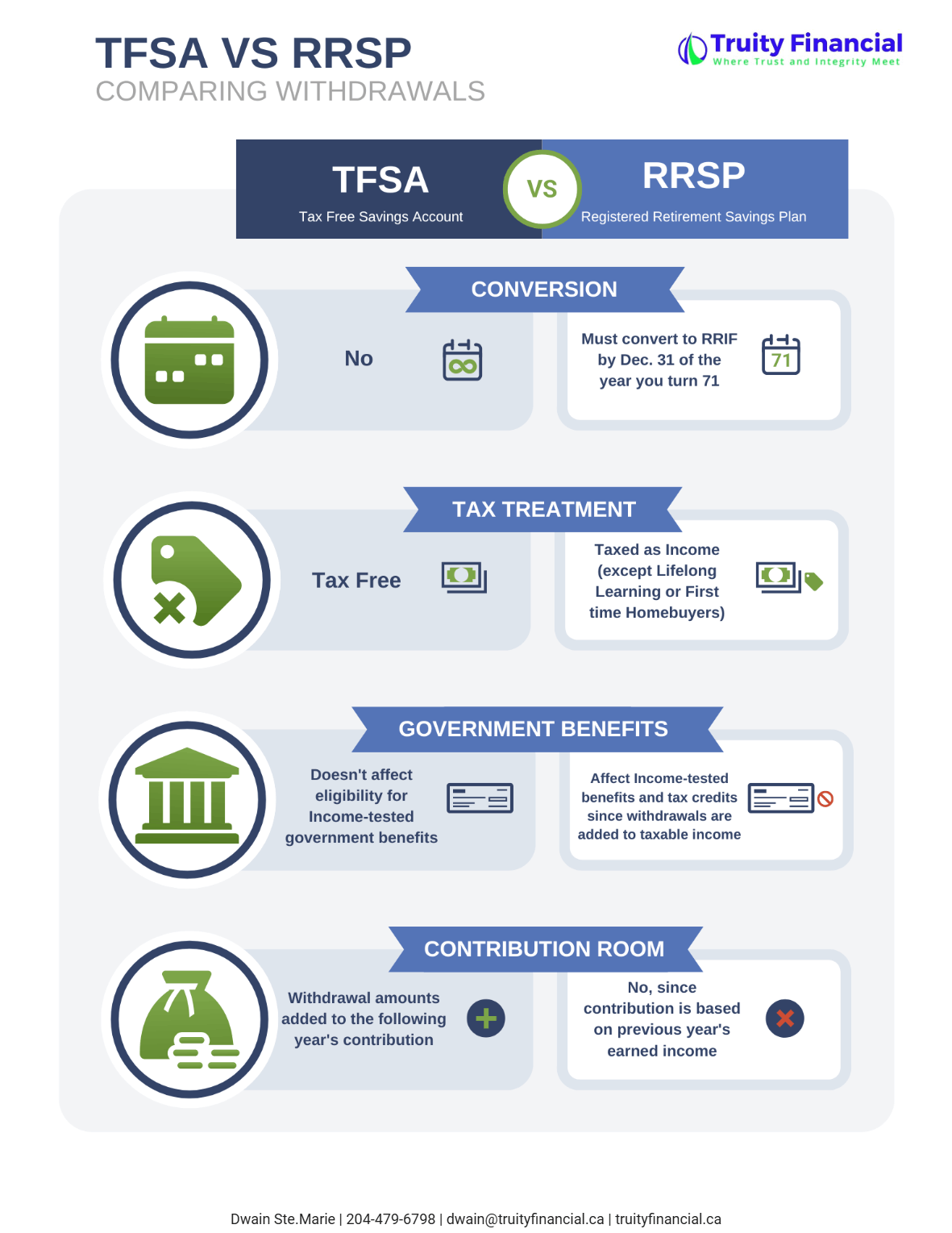
Use a TFSA for Retirement Income
Withdrawals from a Tax-Free Savings Account (TFSA) don’t count toward Line 23400. Drawing income from a TFSA instead of taxable accounts can help preserve your OAS and reduce your tax burden.
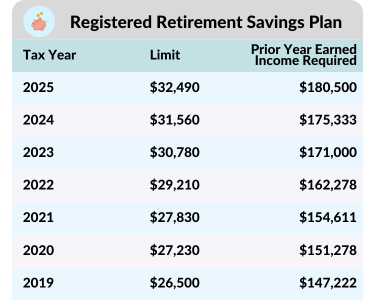
Manage RRIF Withdrawals
RRIF withdrawals are fully taxable and included in Line 23400. If you don’t need the full minimum withdrawal, we may recommend delaying full RRSP-to-RRIF conversion or converting just part each year starting at age 65. This can help smooth your income and avoid large spikes.
Delay OAS or Split Withdrawals Over Time
If you’re planning to delay OAS, we’ll help ensure you’re not unintentionally stacking income in the deferral years. Likewise, we can help you spread RRSP-to-RRIF conversions over several years to avoid unnecessary spikes in income.
Pension Income Splitting
If you’re married or in a common-law relationship, you can split up to 50% of eligible pension income with your spouse. This reduces your taxable income and can keep you below the clawback threshold—especially effective when one spouse earns significantly less.
Choose Tax-Efficient Investments
Not all investment income is taxed equally:
-
Capital gains: 50% taxable; more clawback-friendly
-
Eligible dividends: grossed up for Line 23400 purposes, potentially triggering more clawback despite the tax credit
-
Interest income: fully taxable and the least efficient for minimizing clawback
We can help structure your investments to be as clawback-friendly as possible.
Donate Securities Instead of Cash
Donating appreciated publicly traded securities directly to a registered charity eliminates the capital gains tax, reduces net income, and supports a cause—all while lowering recovery tax exposure.
Defer Large Income Events
Selling a property, realizing a large capital gain, or cashing a pension lump sum can push you into full clawback territory. If possible, we can help you plan these events to spread them over several years or delay them to a lower-income year.
Consider Leveraged Investing
Some higher-net-worth clients use leveraged investment strategies—borrowing to invest in tax-efficient, capital-gains-producing assets. Interest may be deductible, and investment income can be structured to reduce Line 23400. This is a high-risk strategy and something we’ll discuss carefully if appropriate.
Talk to Your Financial Advisor
Everyone’s income, retirement timing, and tax situation are unique. That’s why we take the time to understand your goals, project your Line 23400 income, explore different scenarios, and build a personalized strategy designed to minimize the recovery tax while keeping your lifestyle in mind.
The OAS recovery tax can quietly chip away at your retirement income—but it doesn’t have to. With the right guidance and a plan tailored to you, it’s possible to keep more of what you’ve worked so hard to earn.
If you’re already retired or approaching retirement, now is the perfect time to sit down and talk. Together, we’ll review where you stand, explore your options, and build a strategy that keeps more of your income working for you. We’re here to help you make the most of your retirement—let’s get started.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial, legal, or tax advice. Always consult a qualified professional regarding your specific situation. We are not responsible for any actions taken based on this content.
Sources: Old Age Security Payment Amount – Government of Canada: https://www.canada.ca/en/services/benefits/publicpensions/old-age-security.html
Old Age Security Pension Recovery Tax– Government of Canada: https://www.canada.ca/en/services/benefits/publicpensions/old-age-security/recovery-tax.html










-Dwain%20-Ste.Marie-vX7es2ewnyr9KyZNC.png)
-Dwain%20-Ste.Marie-vX7es2ewnyr9KyZNC.png)