TFSA versus RRSP – What you need to know to make the most of them in 2023
When looking to save money in a tax-efficient manner, Tax-Free Savings Accounts (TFSA) and Registered Retirement Savings Plans (RRSP) can offer significant tax benefits. To assist you in understanding the distinctions, we will compare the following:
-
The differences in deposits between TFSAs and RRSPs
-
The differences in withdrawals between TFSAs and RRSPs
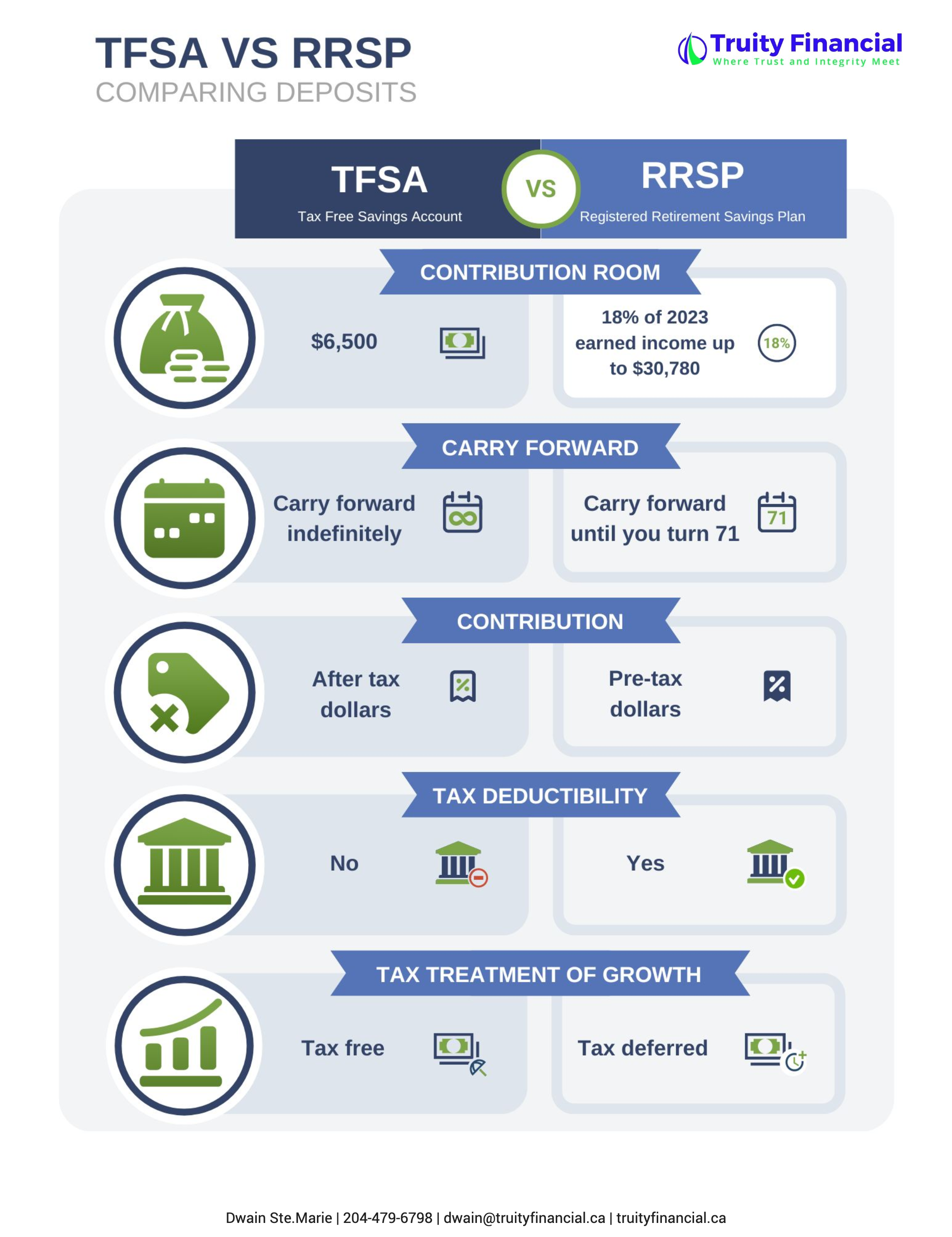
TFSA versus RRSP – Difference in deposits
When comparing deposit differences between TFSAs and RRSPs, there are several key considerations:
-
The amount of contribution room available
-
The ability to carry forward unused contributions
-
The tax deductibility of contributions
-
The tax treatment of growth in the account
How much contribution room do I have?
If you have never contributed to a TFSA, you can contribute up to $88,000 today. This table outlines the contribution amount you are allowed each year since TFSAs were created, including this year:
Regarding RRSPs, the limit for tax deductions is 18% of your pre-tax income from the previous year, with a maximum limit of $30,780. To illustrate, if your pre-tax income in 2022 was $60,000, your deduction limit for 2023 would be $10,800 (18% x $60,000). If your pre-tax income was $200,000, the maximum limit of $30,780 would apply.
How much contribution room can I carry forward?
Suppose you opt not to contribute to your TFSA each year or do not contribute the maximum amount. In that case, you can carry forward your unused contribution room indefinitely, provided you are a Canadian resident, over 18 years of age, and have a valid social insurance number. If you make a withdrawal, the amount withdrawn will be added to your annual contribution room for the next calendar year.
In contrast, for an RRSP, you can carry forward your unused contribution room until age 71. Once you reach 71, you are required to convert your RRSP into an RRIF. Withdrawals from an RRSP do not create additional contribution room.
The tax deductibility of contributions
Your TFSA contributions are not tax-deductible and are made with after-tax dollars.
Your RRSP contributions are tax-deductible and made with pre-tax dollars.
Tax Treatment of Growth
It is essential to contribute to both RRSP and TFSA because of the different tax treatment of the growth within them.
A TFSA is ideal for short-term goals, such as saving for a down payment on a house or a vacation, as its growth is entirely tax-free. When withdrawing from your TFSA, you will not have to pay any income tax on the amount withdrawn. On the other hand, the growth within an RRSP is tax-deferred. This means you will not pay taxes on your RRSP gains until age 71, at which point you convert the RRSP into an RRIF and start withdrawing money.
RRSPs are more suitable for long-term goals such as retirement because, in retirement, you will have a lower income and be in a lower tax bracket, resulting in less tax on your RRIF income.
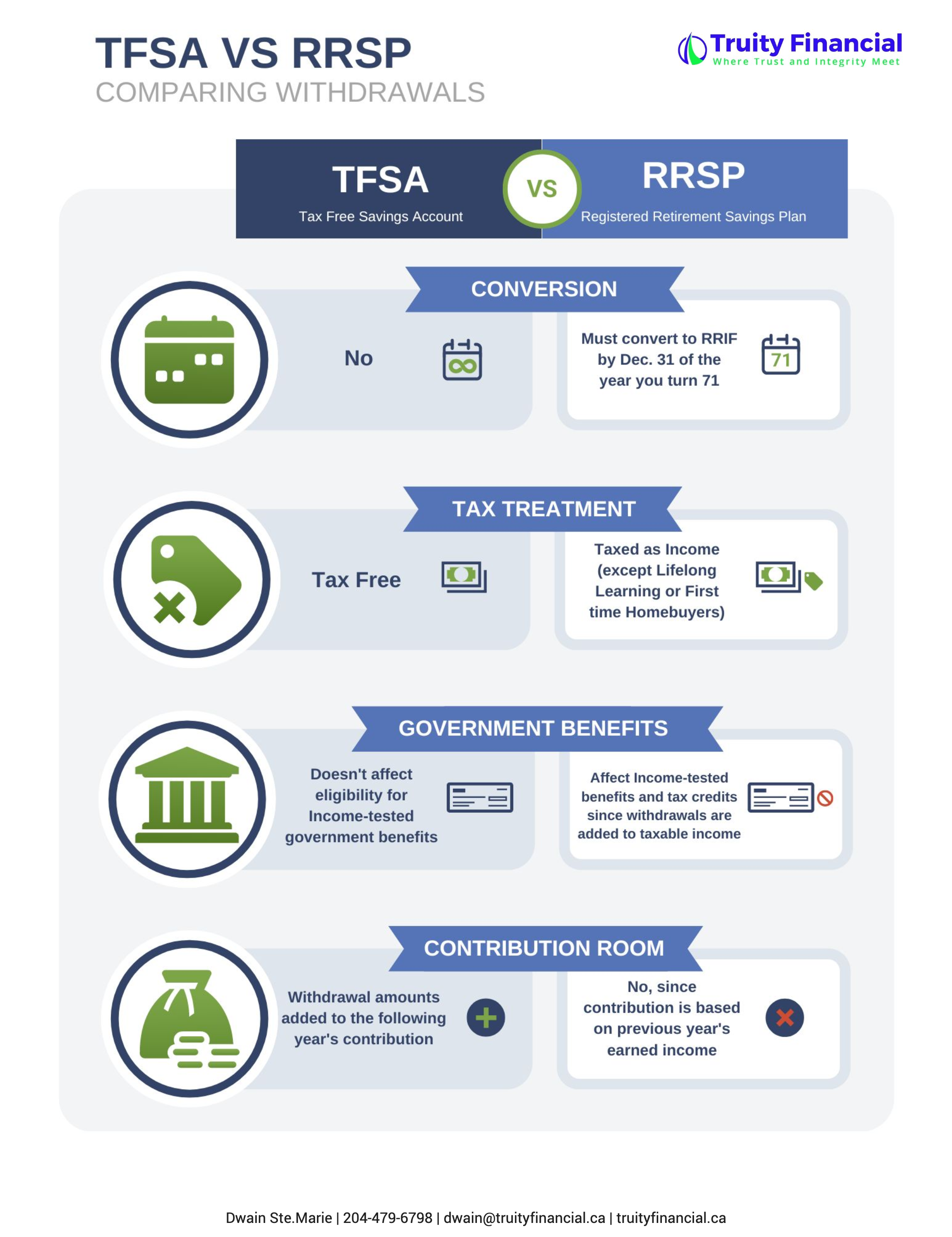
TFSA versus RRSP – Differences in withdrawals
There are several areas to focus on when comparing differences in withdrawal:
-
Conversion Requirements
-
Tax Treatment
-
Government Benefits
-
Contribution Room
Conversion Requirements
For a TFSA, there are never any conversion requirements as there is no maximum age for a TFSA.
For an RRSP, you must convert it to a Registered Retirement Income Fund (RRIF) if you turn 71 by December 31st, 2023.
Tax Treatment of Withdrawals
One of the most attractive things about a TFSA is that all your withdrawals are tax-free! Therefore, they are recommended for short-term goals; you don’t have to worry about taxes when you take money out to pay for a house or a dream vacation.
With an RRSP, if you make a withdrawal, it will be taxed as income except in two cases:
-
The Home Buyers Plan lets you withdraw up to $35,000 tax-free, but you must pay it back within fifteen years.
-
The Lifelong Learning Plan lets you withdraw up to $20,000 ($10,000 maximum per year) tax-free, but you must pay it back within ten years.
How will my government benefits be impacted?
If you are withdrawing from your TFSA or RRSP, it’s essential to know how that will affect any benefits you receive from the government.
Since TFSA withdrawals are not considered taxable income, they will not impact your eligibility for income-tested government benefits.
RRSP withdrawals are considered taxable income and can affect the following:
-
Income-tested tax credits such as Canada Child Tax Benefit, the Working Income Tax Benefit, the Goods and Services Tax Credit, and the Age Credit.
-
Government benefits, including Old Age Security, Guaranteed Income Supplement and Employment Insurance.
How will a withdrawal impact my contribution room?
If you withdraw from your TFSA, the amount you withdrew will be added on top of your annual contribution room for the following calendar year. If you withdraw from your RRSP, you do not open any additional contribution room.
The Takeaway
RRSPs and TFSAs can both be great savings vehicles. However, there are significant differences between them which can affect your finances. If you need help navigating these differences, please do not hesitate to contact us. We’re here to help.